
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, the demand for quicker turnaround times and higher precision has led to the rise of rapid CNC machining as a critical technique. According to the 2022 Industry Report by the International Association of Precision Engineering, rapid CNC machining can reduce production times by up to 75% compared to traditional machining methods while maintaining exceptional accuracy and repeatability. This efficiency is increasingly vital in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where time-to-market and cost-effective production are paramount.
Rapid CNC machining leverages advanced technologies, including computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), to streamline the production process. A recent study from the Global Manufacturing Trends Forum highlights that companies incorporating rapid CNC machining techniques have seen a 40% increase in productivity and a 30% reduction in operational costs. Furthermore, as industries strive for innovation and flexibility in their manufacturing processes, rapid CNC machining is emerging as a key enabler, offering scalability and adaptability to meet diverse production needs.
As we delve into the various strategies and best practices for achieving fast and efficient results through rapid CNC machining, it is essential to understand the technological advancements, material choices, and process optimizations that can further enhance this transformative manufacturing approach. With the right implementation, businesses can harness the full potential of rapid CNC machining to gain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving market landscape.

Rapid CNC machining has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape by providing quicker turnaround times and enhanced precision. Central to this innovation are several key technologies and techniques that facilitate efficient production. One primary method utilized in rapid CNC machining is High-Speed Machining (HSC), which involves the use of higher spindle speeds and feed rates. This approach reduces cycle times significantly while maintaining high accuracy, making it ideal for producing complex parts.
Another essential technique is the implementation of advanced software for Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM). These systems allow for seamless integration between design and machining processes, thereby reducing errors and optimizing tool paths. Furthermore, technologies like additive manufacturing can be combined with CNC machining to create intricate geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional methods.
**Tips:** To enhance efficiency in rapid CNC machining, always ensure your tooling is appropriate for the material being machined and regularly calibrated to uphold performance standards. Additionally, consider using simulation software to predict machining outcomes and identify potential issues before entering the production phase. Lastly, maintaining a clean and organized workspace can significantly improve workflow and reduce downtime, leading to faster project completion.
| Technique | Material Compatibility | Speed (mm/min) | Precision (mm) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Plastics, Metals | 50-300 | 0.1 | Prototypes, Custom Parts |
| CNC Milling | Aluminum, Wood, Plastics | 100-1000 | 0.02 | Complex Shapes, Components |
| CNC Turning | Metals, Plastics | 200-800 | 0.01 | Cylindrical Parts, Shafts |
| EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) | Metals | 20-100 | 0.005 | Hard Materials, Tooling |
Rapid CNC machining has emerged as a critical technology in modern manufacturing, offering significant benefits in terms of speed, precision, and cost efficiency. According to a report by research firm Markets and Markets, the global CNC machining market is projected to grow from $67.45 billion in 2020 to $88.65 billion by 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5%. This growth is largely driven by the need for faster production cycles and the increasing reliance on precision engineering across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
One of the primary advantages of rapid CNC machining is its ability to deliver high precision in a short amount of time. Industry experts indicate that rapid prototyping using CNC techniques can reduce lead times by up to 75%. This efficiency is attributed to advanced machining processes and software that streamline the workflow, enabling manufacturers to quickly iterate designs, decrease the overall time to market, and maintain high standards of quality. Additionally, when compared to traditional machining methods, rapid CNC machining can result in lower per-unit costs, particularly when producing small to medium-sized batches. A study published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology highlights that using CNC processes can reduce material waste by approximately 20% to 30%, further enhancing cost efficiency while promoting sustainable production practices.
In conclusion, the integration of rapid CNC machining into manufacturing processes not only accelerates production timelines but also ensures remarkable cost savings and enhanced quality, making it an invaluable asset for businesses aiming to stay competitive in today's fast-paced market.

In the realm of rapid CNC machining, the choice of materials plays a pivotal role in determining the efficiency and quality of the final output. Common materials used in this process include metals, plastics, and composites, each offering unique advantages and limitations. For instance, aluminum is frequently favored for its lightweight and excellent machinability, making it ideal for prototypes and fixtures. On the other hand, materials such as polycarbonate and nylon are preferred in applications requiring flexibility and impact resistance, showcasing the versatility of CNC machining when adapting to various material properties.
A comparative analysis of these materials reveals that the selection often hinges on the specific requirements of the project, including strength, weight, and thermal stability. While metals can provide superior structural integrity, they may also increase machining time and cost, particularly in complex designs. Conversely, while plastics may lead to faster production timelines, they might not always meet the necessary strength specifications for certain industrial applications. This analysis emphasizes the importance of balancing material selection with design needs, underscoring how the right choice can enhance both the speed and effectiveness of rapid CNC machining, thereby meeting the demands of modern manufacturing processes.
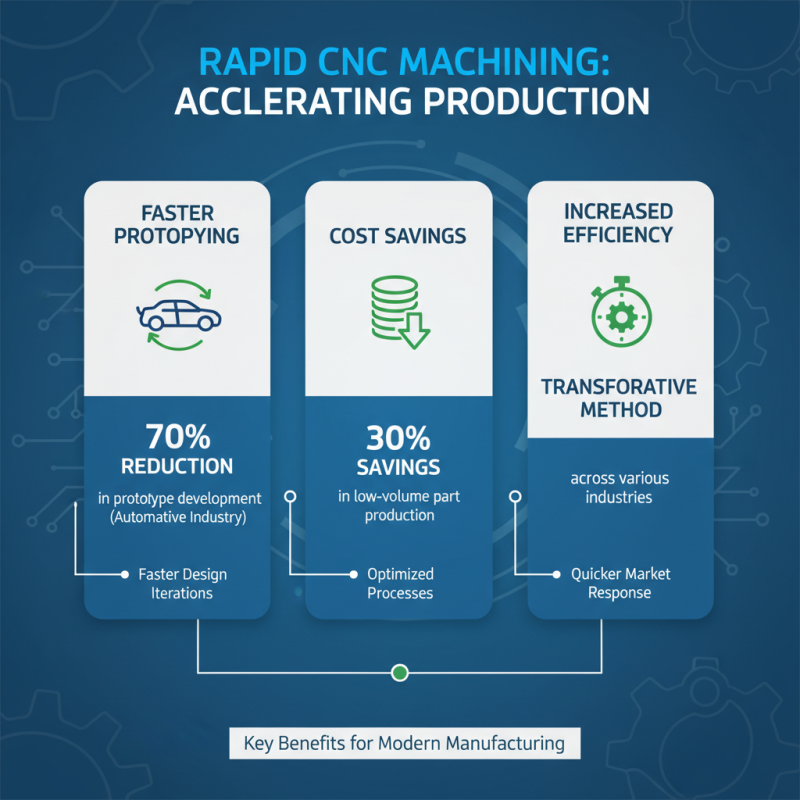
Rapid CNC machining has emerged as a transformative method across various industries, significantly enhancing production efficiency and speed. In automotive manufacturing, for instance, companies have reported a reduction in prototype development times by up to 70% when utilizing rapid CNC techniques. This enables faster design iterations and quicker responses to market demands. A study by the Additive Manufacturing Association indicated that the integration of rapid CNC machining can lead to cost savings of around 30% in low-volume part production, making it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to optimize their processes.
In the aerospace sector, rapid CNC machining allows for the fabrication of lightweight components with intricate geometries that meet demanding specifications. An analysis by aerospace industry experts found that these techniques can reduce material waste by nearly 15%, contributing to more sustainable production practices. For instance, case studies from leading firms showcase how rapid machining has led to the production of critical engine components within tighter tolerances and shorter lead times without compromising quality.
**Tip:** When adopting rapid CNC machining, consider investing in advanced software for real-time simulation and testing. This can significantly enhance accuracy and reduce the likelihood of errors during the machining process.
**Tip:** Collaborate with skilled technicians who specialize in CNC programming. Their expertise can help streamline operations and improve the overall efficiency of your machining projects, ultimately leading to better outcomes and heightened productivity.
The landscape of rapid CNC machining is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and changing market demands. One of the most significant trends is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into CNC processes. These innovations enhance precision, predict maintenance needs, and optimize machining parameters in real-time, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing production times. By automating these processes, manufacturers can achieve faster turnaround times and respond more swiftly to customer needs, facilitating a more agile production environment.
Another emerging trend is the growing use of advanced materials and composite technologies in CNC machining. As industries increasingly seek lighter, stronger materials to enhance product performance, CNC machining techniques are being adapted to work with these innovative materials. This shift not only improves the quality of the final products but also expands the range of applications for CNC machining in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. The market forecast indicates a strong demand for CNC machining services that align with these technological advancements, positioning companies that invest in these capabilities as leaders in a competitive market.







| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |

